Ball and socket joint are present between humerus and pectoral girdle. These joints allows free movement of bone in all direction. e.g., shoulder jointds (humerus bone in socket of pectoral girdle) and hip joints femur bone in socket pelvic girdle.
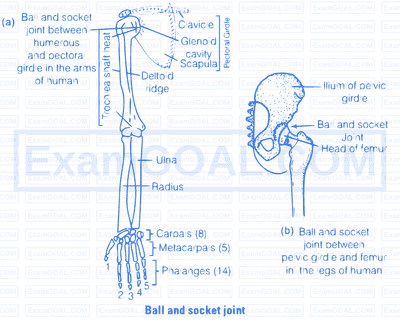
Our forearm is made of three different bones, i.e., humerus, radius and ulna. These bones can be seen in following figure

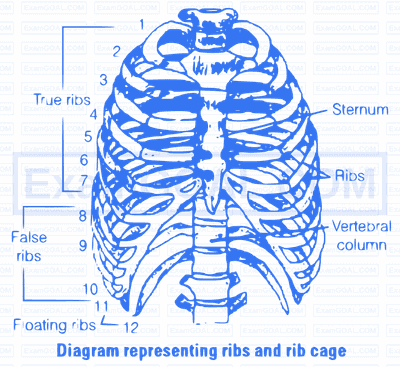
With respect to rib cage, explain the following
(a) bicephalic ribs (b) true ribs (c) floating ribs
(a) Bicephalic ribs, each ribs has two articulating surfaces on its dorsal end hence, are called as bicephalic ribs.
(b) True ribs are the first seven pairs of ribs Dorsally these ribs are attached to the thoracic vertebrae and ventrally connected to the sternum with the help of hyaline cartilage.
(c) Floating ribs are the last two pair (11th and 12th) of ribs and are not connected ventrally to the sternum therefore, called as floating ribs.
Exchange of calcium between bone and extracellular fluid takes place under the influence of certain hormones
(a) What will happen if more of $\mathrm{Ca}^{2+}$ is in extracellular fluid?
(b) What will happen if very less amount of $\mathrm{Ca}^{2+}$ is in the extracellular fluid?
(a) More $\mathrm{Ca}^{2+}$ concentration in extracellular fluid is associated with hyperparathyroidism. It causes demineralisation, resulting in softening and bending of the bones. This condition leads to osteoporosis.
(b) Very less amount of $\mathrm{Ca}^{2+}$ in extracellular fluid is associated with hypoparathyroidism. This increases the excitability of nerves and muscles, causing cramps, sustained contraction of the muscles of larynx, face, hands and feet. This disorder is called parathyroidtetany or hypercalcemictetany.