Match the following columns.
| Column I | Column II | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| A. | Molecular oxygen | 1. | $\alpha$-ketoglutaric acid (1) |
| B. | Electron acceptor | 2. | Hydrogen acceptor (A) |
| C. | Pyruvate dehydrogenase | 3. | Cytochrome-c (B) |
| D. | Decarboxylation | 4. | Acetyl Co - A (C) |
Different substrates get oxidised during respiration. How does Respiratory Quotient (RQ) indicate which type of substrate, i.e., carbohydrate, fat or protein is getting oxidised?
$$\text { R.Q. }=\frac{A}{B}$$
What do $A$ and $B$ stand for?
What type of substrates have R.Q. of $1,<1$ or $>1$ ?
Which of the following will release more energy on oxidation? Arrange them in ascending order.
(a) 1 gm of fat
(b) 1 gm of protein
(c) 1 gm of glucose
(d) 0.5 gm of protein +0.5 gm glucose
Pyruvic acid is the end product of glycolysis. What are the three metabolic fates of pyruvic acid under aerobic and anaerobic conditions? Write in the space provided in the diagram.

Respiration is an energy releasing and enzymatically controlled catabolic process which involves a step-wise oxidative breakdown of organic substances inside living cells. In this statement about respiration explain the meaning of
(a) Step-wise oxidative breakdown
(b) Organic substances (used as substrates).
The figure given below shows the steps in glycolysis. Fill in the missing steps $A, B, C, D$ and also indicate whether ATP is being used up or released at step $E$ ?

RuBP carboxylase, PEPcase, pyruvate dehydrogenase, ATPase, cytochrome oxidase, hexokinase, lactate dehydrogenase. Select/choose enzymes from the list above which are involved in
(a) Photosynthesis (b) Respiration (c) Both in photosynthesis and respiration
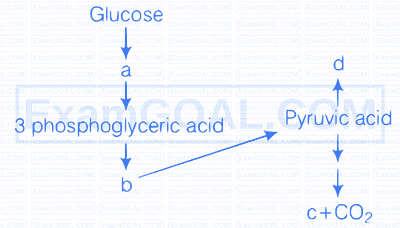
In the following flow chart, replace the symbols $\mathrm{a}, \mathrm{b}, \mathrm{c}$ and d with appropriate terms. Briefly explain the process and give any two application of it.

Given below is a diagram showing ATP synthesis during aerobic respiration, replace the symbols A , $B, C, D$ and $E$ by appropriate terms as given below. F 1 , particle, formation of $\mathrm{Pi}, 2 \mathrm{H}^{+}$, inner mitochondrial membrane, ATP, Fo particle, ADP.