Match the following.
| Column I | Column II | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| A. | IAA | 1. | Herring sperm DNA |
| B. | ABA | 2. | Bolting |
| C. | Ethylene | 3. | Stomatal closure |
| D. | GA | 4. | Weed-free lawns |
| E. | Cytokinins | 5. | Ripening of fruits |
Fill in the places with appropriate word/words.
(a) A phase of growth which is maximum and fastest is ............. .
(b) Apical dominance as expressed in dicotyledonous plants is due to the presence of more ............ in the apical bud than in the lateral ones.
(c) In addition to auxin, a ............ must be supplied to culture medium to obtain a good callus in plant tissue culture.
(d) ............ of a vegetative plants are the sites of photoperiodic perception.
Plant Growth Substances (PGS) have innumerable practical applications. Name the PGS you should use to
(a) increase yield of sugarcane
(b) promote lateral shoot growth
(c) cause sprouting of potato tuber
(d) inhibit seed germination
Gibberellins were first discovered in Japan when rice plants were suffering from bakane (the foolish seedling disease) caused by a fungus Gibberella fujikuroi.
(a) Give two functions of this phytohormone.
(b) Which property of gibberellin caused foolish seedling disease in rice?
Where are the following hormones synthesised in plants?
(a) IAA (b) Gibberellins (c) Cytokinins
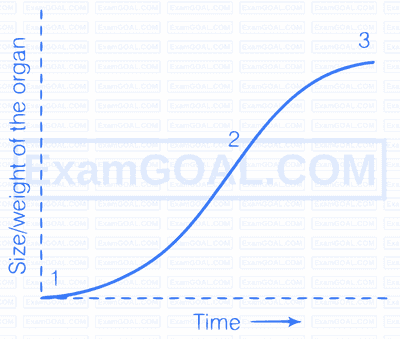
In the figure of sigmoid growth curve given below, label segments 1,2 and 3.
What are the structural characteristics of
(a) meristematic cells near root tip
(b) the cells in the elongation zone of the root
Explain in 2-3 lines each of the following terms with the help of examples taken from different plant tissues.
(a) Differentiation (b) De-differentiation (c) Re-differentiation
Auxins are growth hormones capable of promoting cell elongation. They have been used in horticulture to promote growth, flowering and rooting. Write a line to explain the meaning of the following terms related to auxins.
(a) Auxins precursors (b) Anti-auxins (c) Synthetic auxins
Label the diagram
A. This is which part of a dicotyledonous plants?
B. If we remove part 1 from the plant, what will happen?

On germination a seed first produces shoots with leaves, flowers appear later,
A. Why do you think this happens?
B. How is this advantageous to the plant?
Fill in the blanks
A. Maximum growth is observed in ............. phase.
B. Apical dominance is due to ............
C. ........... initiate rooting .
D. Pigment involved in photoperception in flowering plants in ............ .
It is known that some varieties of wheat are sown in autumn but are harvested around next mid summer.
A. What could be the probable reason for this?
B. What term is used for this promotion of lowering under low temperature?
C. Which plant hormone can replace the cold treatment?
Name a hormone which
A. is gaseous in nature
B. is responsible for phototropism
C. induces femaleness in flowers of cucumber
D. is used for killing weeds (dicots)
E. induces flowering in long day plants.