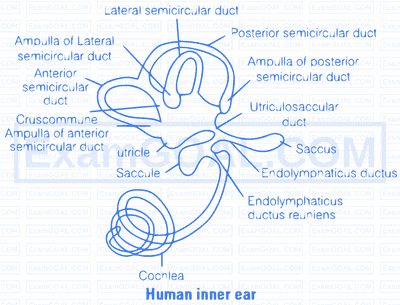
The vestibular system is the sensory apparatus of the inner ear that helps the body maintain its postural equilibrium. There are two sets of organs in inner ear, or labyrinth-The semicircular canals which respond to rotational movements; and the utricle and saccule within the vestibule, which respond to changes in the position of the head with respect to gravity. Each semicircular canal contains hair cells. Rotation of the head causes a flow of fluid, which in turn causes displacement of the top portion of hair cells embedded in jelly-like capula. Utricle and saccule called otolithic organs contain hair cells blanketed with ting stones called otoconia. When the head is tilted or body position is changed the displacement of stones causes the hair cells to bend.
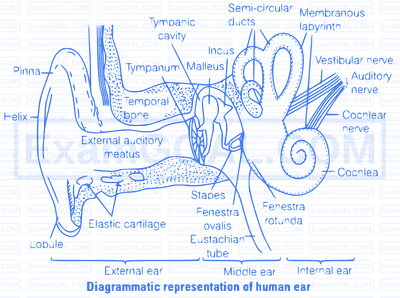
External Auditory canal $\rightarrow$ Eardrum $\rightarrow$ Malleus $\rightarrow$ The reception and transmis sion of sound wares occurs in following order-
Incus $\longrightarrow$ Stapes $\longrightarrow$ Cochlea $\longrightarrow$ Cochlear nerve

The following structures are involved in the protection of brain in animals
(i) Cranium There are 8 cranial bones which form the hard protective outer covering cranium for the brain.
(ii) Meninges The brain is covered with three membranes called meninges.
(a) Piamater Inner most membrane very thin, delicate and vascular and invests the brain closely.
(b) Arachnoid membrane It is like spider we in structure from which its gets its name.
(c) Duramater It is outer most, thick, tough fibrous membrane adhering closely to the inside of the skull.
(iii) Cerebrospinal fluid The cerebrospinal is present in the spaces between the meninges, i.e., arachnoid and duramater, which functions as a pad, absorbing shocks.