Among various enzymatic secretions, gastric juice is released in stomach whereas the bile, pancreatic juice and the intestinal juice are the secretions released into the small intestine. Pancreatic juice and bile are released through the hepato-pancreatic duct. Gastric juice contains hydrochloric acid and proenzyme - pepsinogen and prorennin. HCl maintains a strongly acidic pH which converst these proenzymes into pepsin and rennini (in infants) respectively. These enzymes act on proteins and convert them into simpler form, peptones. The pancreatic juice contains inactive enzymes trypsinogen, chymotrypsinogen, procarboxypeptidases, amylases, lipases and nucleases. Trypsinogen is activated by an enzyme, enterokinase, (secreted by the intestinal mucosa) into active trypsin, which in turn activates the other enzymes in the pancreatic juice. The bile released into the duodenum contains bile pigments (billirubin and billiverdin), bile salts, cholesterol and phospholipids but no enzymes. Bile helps in emulsification of fats, i.e., breaking down of the fats into very small micelles. Bile also activates lipases. The secretions of the brush border cells of the mucosa along with the secretions of the goblet cells constitute the intestinal juice or succus entericus. This juice contains a variety of enzymes like disaccharidases (e.g., maltase), dipeptidases, lipases, nucleosidases, etc. The mucus along with the bicarbonates from the pancreas protects the intestinal mucosa from acid as well as provide an alkaline medium (pH 7.8) for enzymatic activities. Sub-mucosal glands (Brunner's glands) also help in this process. Various reactions involved in this process are as follows
(i) Pepsinogen $\xrightarrow{\mathrm{HCl}}$ Pepsin
Proteins $\xrightarrow{\text { Peptine }}$ Peptones
(ii) Peptones $\xrightarrow[\text { Carboxypeptidase }]{\text { Trypin/Chymotrypsin }}$ Dipeptides
Dipeptides $\xrightarrow{\text { Dipeptidases }}$ Amino acids
(iii) Carbohydrates $\xrightarrow{\text { Amylase }}$ Disaccharides
$$ \begin{aligned} & \text { Maltose } \xrightarrow{\text { Maltase }} \text { Glucose + Glucose } \\ & \text { Lactose } \xrightarrow{\text { Lactase }} \text { Glucose + Galactose } \\ & \text { Sucrose } \xrightarrow{\text { Sucrase }} \text { Glucose + Fructose } \end{aligned}$$
(iv) Fats $\xrightarrow[\text { Hydrolysed }]{\text { Lipases }}$ Diglycerides $\longrightarrow$ Monoglycerides
$$ \begin{aligned} & \text { Di and Monoglycerides } \xrightarrow{\text { Lipases }} \text { Fatty acids + Glycerol } \\ & \text { (v) Nucleic acids } \xrightarrow{\text { Nucleases }} \text { Nucleotides } \\ & \text { Nucleosides } \xrightarrow{\text { Nucleosidases }} \text { Sugars + Bases } \end{aligned}$$
Mechanism of absorption for different molecules is as follow
(i) Small amounts of monosaccarides like glucose, amino acids and some electrolytes like chloride ions are generally absorbed by simple diffusion. The passage of these substances into the blood depends upon the concentration gradient
(ii) Fructose and some amino acids are absorbed with the help of carrier ions like $\mathrm{Na}^{+}$. This mechanism of transport is called facilitated transport or active transport.
(iii) Transport of water depends on osmotic gradient.
(iv) Fatty acids and glycerol being insoluble, cannot be absorbed into the blood. They are first incorporated into micelles (smalll droplets) which move into intestinal mucosa.
Further, they are reformed into protein coated fat globules called chylomicrons which are transported to the lymph vessels in the villi. These lymph vessels ultimately release the absorbed substances into the blood stream.
This bile duct (from gall bladder and liver) and the pancreatic duct (from pancreas) releases pancreatic juice and bile into the duodenum through the common hepato-pancreatic duct which is guarded by a sphincter called sphincter of Oddi.
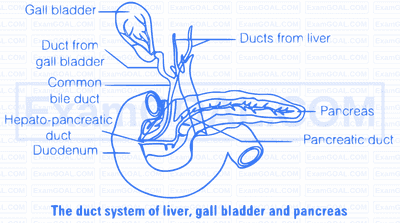
The pancreatic juice contains inactive enzymes, i.e., trypsinogen, chymotrypsinogen, procarboxypeptidase, amylase, lipases and nucleases.
The action of hepato-pancreatic secretion on digestion on carbohydrate, proteins and fats are summarised below
(i) Carbohydrates in the chyme are hydrolysed by pancreatic amylase into disaccharides.
Polysaccharides (starch) $\xrightarrow{\text { Pancreatic amylase }}$ Disaccharides
(ii) Fats are broken down by lipases with the help of bile into di and monoglycerides.
Triglycerides $\xrightarrow{\text { Bile }}$ Emulsified triglycerids $\xrightarrow{\text { Lipase }}$ Diglycerides $\longrightarrow$ Monoglycerides
(iii) Proteins in the chyme reaching the intestine are acted upon by the proteolytic enzymes of pancreatic juice.
Proteins Peptones $\frac{\text { Trypsin/Chymotrypsin }}{\text { Carboxy peptidase }}$ Dipeptides Proteoses
The buccal cavity performs two major functions i.e., mastication of food and facilitation of swallowing
Firstly, food gets mixed with saliva which softens and lubricates the food and cheuring process breaks the food into smaller pieces. Buccal cavity is also involved in the digestion of same food components.
Digestion of carbohydrates starts in the buccal cavity. The food is mixed with saliva which contains salivary anylase. This enzyme converts starch into maltose, isomaltose and $\alpha$-dextrins. $30 \%$ of the starch in food is hydorlysed in the buccal cavity.
Starch $\xrightarrow[\text { anylase }]{\text { Salivany }}$ Maltose + Isomaltose $+\alpha$-dextrins
Saliva do not any protein or fat digesting anzyme. Therefore, their digestion do not occur in the oral cavity.
The oral cavity has a number of teeth and a muscular tongue. Each tooth is embedded in a socket of jaw bone.
This type of attachement is called thecodont. The human have two sets of teeth a temporary and a permenant. This type of denotation is called diphyodont. The arrangement of teeth is illustrated below.
