For completion of respiration process, write the given steps in sequential manner.
(a) Diffusion of gases ( $\mathrm{O}_2$ and $\mathrm{CO}_2$ ) across alveolar membrane.
(b) Transport of gases by blood.
(c) Utilisation of $\mathrm{O}_2$ by the cells for catabolic reactions and resultant release of $\mathrm{CO}_2$.
(d) Pulmonary ventilation by which atmospheric air is drawn in and $\mathrm{CO}_2$ rich alveolar air is released out.
(e) Diffusion of $\mathrm{O}_2$ and $\mathrm{CO}_2$ between blood and tissues.
(d) Pulmonary ventilation by which atmospheric air is drawn in and $\mathrm{CO}_2$ rich alveolar air is released out.
(a) Diffusion of gases $\left(\mathrm{O}_2\right.$ and $\left.\mathrm{CO}_2\right)$ across alveolar membrane.
(b) Transport of gases by blood.
(c) Diffusion of $\mathrm{O}_2$ and $\mathrm{CO}_2$ between blood and tissues.
(e) Utilisation of $\mathrm{O}_2$ by the cells for catabolic reactions and resultant release of $\mathrm{CO}_2$.
Differentiate between
(a) Inspiratory and expiratory reserve volume
(b) Vital capacity and total lung capacity.
(c) Emphysema and occupational respiratory disorder.
Difference between these are as follows
| (a) | Inspiratory Reserve Volume | Expiratory Reserve Volume |
|---|---|---|
| It is the additional volume of air, a person can inspire by a forcible inspiration. It ranges between 2500 mL to 3000 mL . | It is the additional volume of air a person can expire by a forcible expiration. It ranges between 1000 mL to 1100 mL . | |
| (b) | Vital Capacity | Total Lung Capacity |
| Vital capacity is the maximum volume of air that a person can breathe in after a forced expiration. This includes ERV, TV and IRV or the maximum volume of air a person can breathe out after a forced inspiration. i.e., $\mathrm{Vc}=\mathrm{ERV}+\mathrm{IRV}+\mathrm{TV}$ | Total using capacity is the total volume of air accommodated in the lungs at the end of a forced inspiration. This includes RV, ERV, TV and IRV or vital capacity + residual volume. i.e., $\mathrm{TLC}=\mathrm{RV}+(\mathrm{ERV}+\mathrm{IRV}+\mathrm{TV})$ or $\mathrm{VC}+\mathrm{RV}$ | |
| (c) | Emphysema | Occupational Respiratory Disorder |
| Emphysema is a chronic disorder of respiratory system, in which alveolar cells are damaged due to which regulatory respiratory surface is decreased. Cause of emphysema is cigarette smoking. |
It is caused due to the long exposure of dust produced by stone grinding or breaking and give rise to inflammation leading to fibrosis and thus causing serious lung damage. Protective masks are provided for the workers in such industries. |
Representing the transport of $\mathrm{O}_2$ and $\mathrm{CO}_2$ between alveoli and tisue with diagram

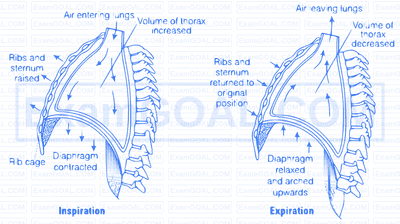
Mechanism of Breathing Breathing involves two stages, inspiration during which atmospheric air is drawn in and expiration by which the alveolar air is released out. The movement of air into and out of the lungs is carried out by creating a pressure gradient between the lungs and the atmosphere, the help of diaphragm and inter costal muscles.
Human beings have a significant ability to maintain and moderate the respiratory rhythm to suit the demands of the body tissue. This is done by the neural system.
Respiration regulated by neural system in following ways/ manress
(i) A specialised centre present in the medulla region of the brain called respiratory rhythm centre is primarily responsible in regulating respiration process. Another centre present in the pons region of the brain called pneumotaxic centre, can moderate the functions of the respiratory rhythm centre. Neural signal from this centre, can reduce the duration of inspiration and thereby alter the respiratory rate.
(ii) A chemosensitive area is situated adjacent to the rhythm centre which is highly sensitive to $\mathrm{CO}_2$ and hydrogen ions. Increase in these substances activates this centre, which in turn signals the rhythm centre to make necessary adjustments in the respiratory process by which these substances can be eliminated.
(iii) Receptors associated with aortic arch and carotid artery also recognise changes in $\mathrm{CO}_2$ and $\mathrm{H}^{+}$concentration and send necessary signals to the rhythm centre for remedial action because the role of oxygen in the regulation of respiratory rhythm is quite insignificant.