Electrocardiograph (ECG) is a graphical representation of the electrical activity of the heart during a cardiac cycle. A patient is connected to the machine with three electrical leads (one to each wrist and one to the left ankle) that continuously monitor the heart activity. For a detailed evaluation of the heart functions multiple leads are attached to the chest region.
The QRS complex represents the depolarisation of the ventricles, which initiates the ventricular contraction. The contraction starts shortly after $Q$ and marks the beginning of the systole. The time taken in QRS complex is 0.12 second in normal ECG.
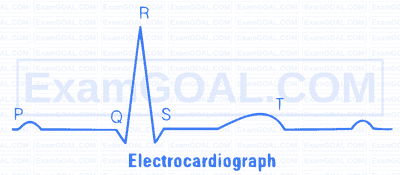
The larger Q and R wave indicate a myocardial infarction (heart attack). The S-T segment is elevated in acute myocardial infarction and depressed when the heart muscle receives insufficient oxygen.
The structure of heart of fishes, reptiles, birds and mammals show many structures of evolutionary significance. Thicker walls of ventricles is one of them.
Ventricles have thick walls because these are mainly involved in pumping the blood to the body parts with certain pressure.
The walls of the left ventricle is about 3 times thicker from the right ventricle, while the atria acts as a collecting chambers for the blood which is starting to the heart thus have thin walled. Also they have to force the blood into the ventricles that lies just below there thus atria have thin walls.

Differentiate between
(a) blood and lymph (b) basophils and eosinophils (c) tricuspid and bicuspid valve
(a) Difference between blood and lymph are as follows
| Blood | Lymph |
|---|---|
| Blood is a connective tissue which have erythrocytes leucocytes and platelet present in fluid called plasma. It flows in all blood vessels. |
Lymph is also a connective tissue which, is devoid of RBC but has large number of WBC (leucocytes) in plasma. It flows only in lymphatic system and is also found extracelluarly inside the tissue. |
(b) Difference between basophils and eosinophils are as follows
| Basophils | Eosinophils |
|---|---|
| These possess 3 lobed nucleus, with less number of coarse granules. These take basic stain. These are normally $0-1 \%$ is the blood. |
These possess bilobed nucleus and coarse granules in cytoplasm These take acidic stain These are $1-6 \%$ is the blood. |
(c) Difference between tricuspid valve and bicuspid valve are as follows
| Tricuspid Value | Bicuspid Value |
|---|---|
| This valve separate the right atria from right ventricle. It is made of 3 cusps or flaps. This is also known as right atrio ventricular valve. |
This valve separates the left atria from left ventricle. It has 2 cusps or flaps. This is also called mitral valve or left atrio ventricular valve. |
Briefly describe the followings
(a) anaemia
(b) angina pectoris
(c) atherosclerosis
(d) hypertension
(e) heart failure
(f) erythroblastosis foetalis
(a) Anaemia is the decrease in the number of RBC than the normal amount and also due to less quantity of haemoglobin than the normal value in blood This is the most common disorder of the blood.
(b) Angina Pectoris Ocurs when there is blockage in coronary artery, thus in sufficient supply of blood reaches to heart muscles. This results in chest pain, fear, anxiety, pale skin, profuse sweating and vomitting. The anginal pain usually starts in the centre of the chest spreads down to the left arm which last for only few second.
(c) Atherosclerosis is the deposition of cholesterol in the inner lining of arteries called atherosclerotic plaque. Sometimes arteries are completely blocked, this result in stroke or heart attack.
(d) Hypertension Ps sometimes also called as arterial hypertension. The blood pressure in the arteries getselevated. It could be primary hypertension which has no obvious medical reason but secondary hypertension are caused by various conditions which affect kidneys, arteries heart or endocrine system.
(e) Heart Failure is the state of heart when it does not pump blood effectively enough to meet the needs of the body.
(f) Erythroblastosis foetalis is a haemolytic disease of new borns which is an allo-immune condition that develops in foetus when IgG molecules produced by mother pass through placenta and attack RBC causing reticulocytosis and anaemia. It develops due to Rh incompatibility between the couples. In a man with $\mathrm{RH}^{+}$blood and women with $\mathrm{Rh}^{-}$, blood the second pregnancy foetus may have this problem due to IgG accumulation in women during first child development and delivery.
The birds and mammals have evolutionary advancement as far as structure of heart is concerned. They need more oxygen to live in terrestrial habitat.
In these animals, the blood received by left and right auricles is oxygenated and deoxygenated respectively. It passes towards the left and right ventricles and thus no oxygenated and deoxygenated blood is mixed. The ventricles pump oxygenated deoxygenated blood without mixing.
Thus, two separate circulatory pathways are found thus this type of blood circulation is called as double circulation, which include systemic and pulmonary circulation.
