Electrocardiograph (ECG) is a graphical representation of the electrical activity of the heart during a cardiac cycle. A patient is connected to the machine with three electrical leads (one to each wrist and one to the left ankle) that continuously monitor the heart activity. For a detailed evaluation of the heart functions multiple leads are attached to the chest region.
The QRS complex represents the depolarisation of the ventricles, which initiates the ventricular contraction. The contraction starts shortly after $Q$ and marks the beginning of the systole. The time taken in QRS complex is 0.12 second in normal ECG.
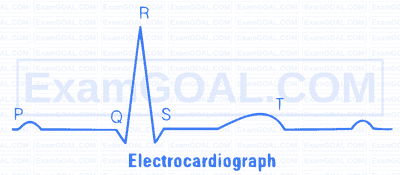
The larger Q and R wave indicate a myocardial infarction (heart attack). The S-T segment is elevated in acute myocardial infarction and depressed when the heart muscle receives insufficient oxygen.
The structure of heart of fishes, reptiles, birds and mammals show many structures of evolutionary significance. Thicker walls of ventricles is one of them.
Ventricles have thick walls because these are mainly involved in pumping the blood to the body parts with certain pressure.
The walls of the left ventricle is about 3 times thicker from the right ventricle, while the atria acts as a collecting chambers for the blood which is starting to the heart thus have thin walled. Also they have to force the blood into the ventricles that lies just below there thus atria have thin walls.
