$$ \text { Discuss briefly how a probe is used in molecular diagnostics. } $$
Early detection of a disease is not possible by conventional diagnostic methods. So, some techniques have been implanted for early diagnosis like PCR, recombinant DNA technology and ELISA.
In recombinant DNA technology, a probe is used. It is allowed to hybridise to its complementary DNA in the clone of cells. The cells are then detected by autoradiography.
The cell with mutated gene will not be observed on the photographic film because, the probe will not have complementarity with the mutated gene.
Who was the first patient to be treated with gene therapy? Why was the given treatment recurrent in nature?
Gene therapy is a collection of methods that allows the correction of gene defects diagnosed in a child or embryo. Correction of a genetic defect involves the delivery of a normal gene into the individual or embryo to take over the function of and compensate for the non-functional gene.
The first clinical gene therapy was given in 1990 to a 4 yrs old girl with Adenosine Deaminase (ADA) deficiency.
ADA deficiency is caused due to the deletion of gene for Adenosine Deaminase. It can be cured by bone marrow transplantation or by enzyme replacement therapy. In both the approaches, it is not completley curable.
It may recurrent in nature because in the process of gene therapy, lymphocytes used are found to be mortal in nature and the patient requires periodic infusion of such genetically engineered lymphocytes.
For permanent cure, gene isolated from the bone marrow cells producing ADA is introduced into the cells at early embryonic stages.
Taking examples under each category, discuss upstream and downstream processing.
The fermentation process is the basis of many industries in order to produce diverse products. Fermentation means a process in which microorganisms that are cultured on a large scale, convert a substrate into a product which is useful to human.
The fermentation process is divided into two stages namely Upstream and downstream processing both of these processes can be discussed taking an example of citric acid production.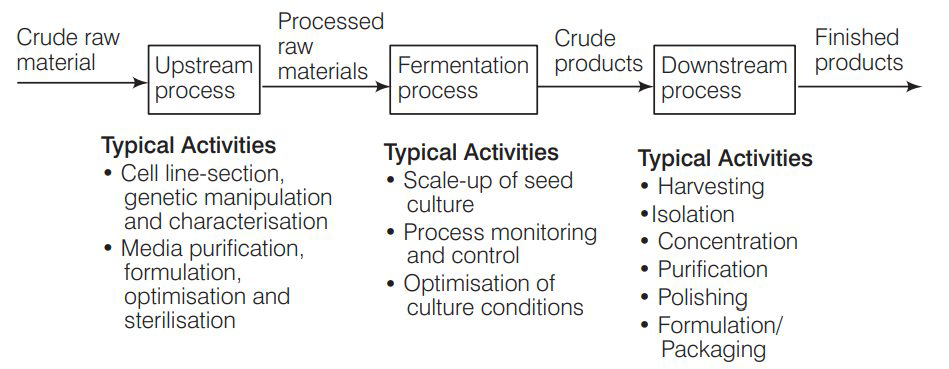 The upstream processing in biotechnology involves identifying a material. This forms the initial process of fermentation. It deals with inoculum preparation, preparation of culture media, scale up of the entire process and inoculation.
The upstream processing in biotechnology involves identifying a material. This forms the initial process of fermentation. It deals with inoculum preparation, preparation of culture media, scale up of the entire process and inoculation.
When the products are subjected to a series of processes including separation and purification of the product, it is collectively known as downstream processing. It deals with the post-harvest product, i.e., recovery-clarification, purification, polishing and formulation till the packaging of the desired product.
Define antigen and antibody. Name any two diagnostic kits based upon them.
An antigen is a foreign substance that elicits the immune response and results in the formation of an antibody.
Antibody is a protein that is synthesised by the body in response to an antigen.
Antigen and antibody shows high degree of specificity in binding to each other.
Two diagnostic kits based on antigen-antibody interaction are
(a) ELISA for HIV.
(b) Pregnancy test kits.
ELISA technique is based on the principles of antigen-antibody interaction. Can this technique be used in the molecular diagnosis of a genetic disorder, such as phenylketonuria?
Yes, one can use antibody against the enzyme (that is responsible for the metabolism of phenylanaline) to develop ELISA based diagnostic technique. The patient, in which the enzyme-protein complex is absent would give a negative result in ELISA when compared to the normal individual.