How is a mature, functional insulin hormone different from its pro-hormone form?
Mature functional insulin is obtained by the processing of pro-hormone which contains an extra peptide called C -peptide or connecting peptide.
It connects the A and B chains in proinsulin. This C -peptide is removed during the maturation of pro-insulin to insulin and A and B chains gets linked by disulphide linkage.

Gene therapy is an attempt to correct a genetic defect by providing a normal gene into the individual. By this the normal function can be restored. An alternate method would be to provide the gene product (protein/enzyme) known as enzyme replacement therapy, which would also restore the function. Which in your opinion is a better option? Give reason for your answer.
Gene therapy would be a better option because it has the potential to completely cure the patient. It is because the correct gene once introduced in the patient, can continue to produce the correct protein enzyme. Enzyme therapy does not offer permanent cure as it needs to be given to the patient on regular basis. It is also more expensive.
Transgenic animals are the animals in which a foreign gene is expressed. Such animals can be used to study the fundamental biological process, phenomenon as well as for producing products useful for mankind. Give one example for each type.
Transgenic animals are the animals in which a foreign genes are expressed. Such animals can be used to study the fundamental biological process/phenomenon, e.g., by using model organisms like mouse we can determine how genes are regulated (gene regulation), how they affect the normal functions of the body and its development, etc.
Transgenic animals are also used for producing products useful for mankind, e.g., Transgenic cow (rosie). Which produced human protein enriched milk $(2.4 \mathrm{~g} / \mathrm{L})$. The milk contained the human alpha-lactalbumin and was nutritionally a more balanced product for human babies than natural cow-milk.
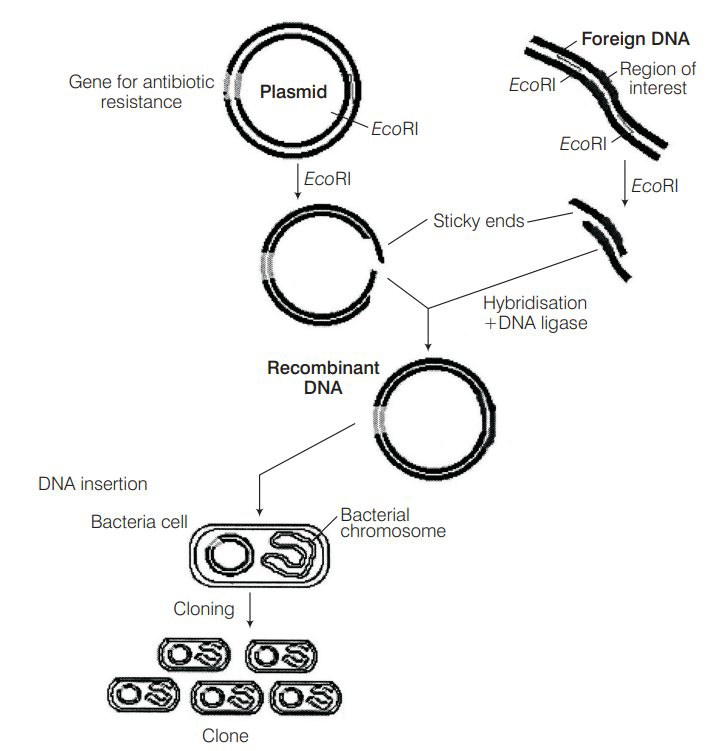
When a foreign DNA is introduced into an organism, how is it maintained in the host and how is it transferred to the progeny of the organism?
Foreign gene is usually ligated to a plasmid vector and introduced in the host. As plasmid replicates, and makes multiple copies of itself, so does the foreign gene gets replicated and its several copies are made. When the host organism divides, its progeny also receives the plasmid. DNA containing the foreign gene.
The whole process can be visualised in the figure given below
Bt cotton is resistant to pest, such as lepidopteran, dipterans and coleopterans. Is Bt cotton also resistant to other pests as well?
Bt cotton is made resistant to certain specific taxa of pests (lepidopteran, dipterans and coleopterans). It is quite likely that in future, some other pests may infest these Bt-cotton plants. It is similar to immunisation against smallpox which does not provide immunity against other pathogens like those, that causes cholera, typhoid etc.