9
MCQ (Multiple Correct Answer)
$A B C D E F G H$ is a hollow cube made of an insulator (figure) face $A B C D$ has positive charge on it. Inside the cube, we have ionised hydrogen. The usual kinetic theory expression for pressure

A
will be valid
B
will not be valid, since the ions would experience forces other than due to collisions with the walls
C
will not be valid, since collisions with walls would not be elastic
D
will not be valid because isotropy is lost
10
MCQ (Multiple Correct Answer)
Diatomic molecules like hydrogen have energies due to both translational as well as rotational motion. From the equation in kinetic theory $p V=\frac{2}{3} E, E$ is
A
the total energy per unit volume
B
only the translational part of energy because rotational energy is very small compared to the translational energy
C
only the translational part of the energy because during collisions with the wall pressure relates to change in linear momentum
D
the translational part of the energy because rotational energies of molecules can be of either sign and its average over all the molecules is zero
11
MCQ (Multiple Correct Answer)
In a diatomic molecule, the rotational energy at a given temperature
A
obeys Maxwell's distribution
B
have the same value for all molecules
C
equals the translational kinetic energy for each molecule
D
is $(2 / 3)$ rd the translational kinetic energy for each molecule
12
MCQ (Multiple Correct Answer)
Which of the following diagrams (figure) depicts ideal gas behaviour?
A

B

C
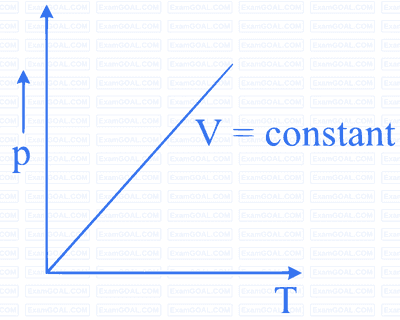
D

13
MCQ (Multiple Correct Answer)
When an ideal gas is compressed adiabatically, its temperature rises the molecules on the average have more kinetic energy than before. The kinetic energy increases,
A
because of collisions with moving parts of the wall only
B
because of collisions with the entire wall
C
because the molecules gets accelerated in their motion inside the volume
D
because of redistribution of energy amongest the molecules